Network Segmentation Analysis
Tripl-i Network Segmentation Analysis provides comprehensive visibility into traffic flows between network zones, enabling security teams to identify unauthorized communications, policy violations, and potential security risks across your infrastructure.
What is Network Segmentation Analysis?
Network Segmentation Analysis is an automated process of:
- Visualizing traffic flows between network zones
- Detecting unauthorized cross-zone communications
- Identifying policy violations in real-time
- Investigating specific connections IP-by-IP
- Enforcing security boundaries between network segments
Why Network Segmentation Matters
Key Features
Traffic Flow Visualization
View cross-zone traffic in multiple formats:
| View Mode | Best For | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sankey Diagram | Executive overview | Visual flow diagram showing traffic volumes between zones |
| Matrix View | Detailed analysis | Tabular view with connections, ports, and violation status |
| List View | Quick scanning | Card-based view for rapid assessment |
Zone Configuration
Define security zones based on your network topology:
Zone Types:
- Production: Critical business systems
- DMZ: Internet-facing services
- Management: Administrative access
- Workstation: End-user devices
- IoT: Internet of Things devices
- Guest: Visitor network access
- Development: Development environments
- Staging: Pre-production testing
- Backup: Data backup systems
Security Levels:
- Critical: Highest protection required
- High: Significant security controls
- Medium: Standard security measures
- Low: Basic security requirements
Violation Detection
Automatically identify unauthorized traffic:
IP-by-IP Investigation
Drill down into specific violations to see:
- Source IP addresses
- Target IP addresses
- Connection counts
- Destination ports
- Process names (when available)
Dashboard Overview
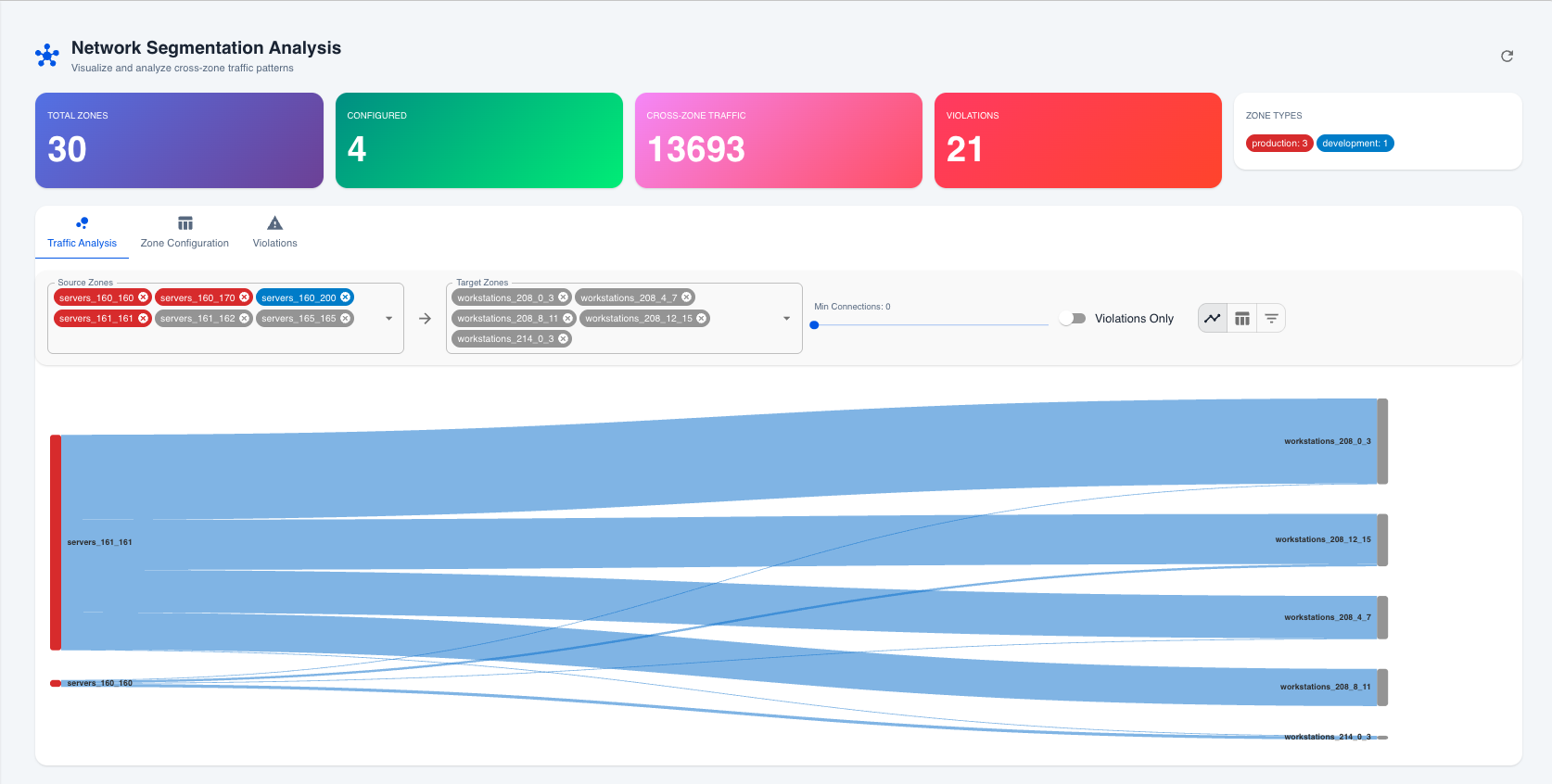 Network Segmentation Analysis dashboard showing traffic flows between zones
Network Segmentation Analysis dashboard showing traffic flows between zones
Summary Cards
The dashboard displays key metrics at a glance:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Total Zones | Number of network zones configured |
| Configured | Zones with security policies defined |
| Cross-Zone Traffic | Total connections between different zones |
| Violations | Number of policy violations detected |
Traffic Analysis Tab
Filters Available:
Source Zones: Multi-select filter for traffic origin
Target Zones: Multi-select filter for traffic destination
Min Connections: Slider to filter by connection volume
Violations Only: Toggle to show only violations
View Options:
- Flow Diagram (Sankey)
- Matrix View (Table)
- List View (Cards)
Zone Configuration Tab
Manage zone security settings:
| Setting | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Zone Type | Classification (Production, DMZ, etc.) |
| Security Level | Priority level (Critical, High, Medium, Low) |
| Allowed Inbound | Zones permitted to connect TO this zone |
| Description | Human-readable zone description |
| Color | Visual identifier for dashboards |
Violations Tab
Investigate security violations:
- Violation List: All detected policy violations with severity
- Investigation Panel: Detailed connection information
- Remediation Guidance: Suggested actions to resolve
 Violations tab showing IP-by-IP connection details for investigation
Violations tab showing IP-by-IP connection details for investigation
How Zones Are Created
Network zones are automatically created from your Discovery Schedules:
Each discovery schedule defines:
- IP Range: The network subnet (e.g.,
10.160.160.0/24) - Zone Name: Auto-generated or custom name
- Agent: The discovery agent managing this zone
Violation Rules
How Violations Are Detected
Violations are calculated in real-time based on zone configuration:
Violation Logic:
IF: Target zone has "Allowed Inbound" configured
AND: Source zone is NOT in the allowed list
THEN: Traffic is flagged as violation
Example:
Target Zone: Production Servers
Allowed Inbound: [Management Zone, Backup Zone]
Traffic from Workstation Zone → Violation (not allowed)
Traffic from Management Zone → Allowed (in list)
Severity Levels
| Severity | Trigger | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| High | Traffic to Critical security level zones | Immediate investigation |
| Medium | Traffic to other protected zones | Review within 24 hours |
| Low | Minor policy deviations | Monitor and assess |
Common Use Cases
Use Case 1: PCI-DSS Compliance
Ensure cardholder data environments are properly segmented:
Scenario:
- Payment Zone: Contains card processing systems
- Allowed Inbound: Only from Web DMZ
Benefit:
- Automatically detect any unauthorized access attempts
- Provide audit evidence of segmentation
- Alert on compliance violations
Use Case 2: Ransomware Prevention
Limit lateral movement opportunities:
Scenario:
- Workstation Zone: End-user devices
- Server Zone: Critical infrastructure
- Allowed Inbound: Only Management Zone to Server Zone
Benefit:
- Detect if compromised workstation contacts servers directly
- Early warning of potential ransomware spread
- Reduced attack surface
Use Case 3: IoT Security
Isolate potentially vulnerable IoT devices:
Scenario:
- IoT Zone: Cameras, sensors, smart devices
- Allowed Outbound: Only to Management Zone
Benefit:
- Detect unauthorized IoT communications
- Prevent IoT devices from accessing sensitive systems
- Identify compromised IoT devices
Best Practices
1. Zone Design
- Principle of Least Privilege: Only allow necessary connections
- Defense in Depth: Layer multiple zones for critical systems
- Logical Grouping: Group similar systems together
2. Policy Configuration
- Start Restrictive: Begin with minimal allowed connections
- Document Exceptions: Record why each allowed connection exists
- Regular Review: Audit zone policies quarterly
3. Violation Response
- Prioritize by Severity: Address high-severity first
- Investigate Thoroughly: Use IP-by-IP analysis
- Update Policies: Add legitimate traffic to allowed lists
- Block Unauthorized: Implement firewall rules for true violations
4. Continuous Monitoring
- Daily Reviews: Check violation summary daily
- Trend Analysis: Monitor violation counts over time
- Alert Integration: Connect to SIEM/SOAR for automated response
Integration with Other Modules
Discovery Module
Network zones are created from discovery schedules, ensuring:
- Automatic zone creation as networks are discovered
- Up-to-date IP range information
- Consistent naming and organization
Event Management
Violations can generate events for:
- Automated incident creation
- Alert correlation
- Response workflow triggers
Compliance Module
Segmentation data supports:
- PCI-DSS requirement evidence
- HIPAA network isolation verification
- Custom compliance framework mapping
Troubleshooting
No Zones Displayed
Cause: No discovery schedules configured
Solution: Create discovery schedules with IP ranges
Cause: Tenant isolation issue
Solution: Verify correct tenant is selected
No Traffic Data
Cause: No network connections collected
Solution: Ensure discovery agents are collecting network data
Cause: IP ranges don't match connections
Solution: Verify zone IP ranges cover actual device IPs
Unexpected Violations
Cause: Allowed Inbound not configured
Solution: Define which zones should be allowed access
Cause: Stale zone configuration
Solution: Review and update zone policies
Next Steps
- Configure Zones: Set zone types and security levels
- Define Policies: Configure allowed inbound connections
- Monitor Traffic: Review cross-zone traffic regularly
- Investigate Violations: Use IP-by-IP analysis for incidents
- Integrate Alerts: Connect violations to your incident workflow