Analyze Service Using Patterns
If you need to find a specific instance of a known service (e.g., "I want to find the Finance Department's Exchange Server"), you can use the Pattern-Based Discovery workflow. This method allows you to select a pre-defined template and run a targeted discovery for that specific service.
Understanding Service Patterns
A Service Pattern is a blueprint that tells the system how to identify a complex business service. It solves the problem of distinguishing between a generic server and a specific business function.
How Patterns Match
The system uses a "Fingerprint" approach to identify servers. A server is considered a match if it meets the criteria defined in the pattern. The matching logic generally uses an OR condition across different types of indicators:
- Software Keywords: Checks the installed software inventory (e.g., "Microsoft Exchange", "Oracle Database").
- Process Signatures: Checks the running process list (e.g.,
sqlservr.exe,tomcat.exe). - Hostname Patterns: Checks the server name (e.g., servers named
*exch*or*sql*).
If a server matches any of these high-confidence indicators, it is flagged as a potential component of the service.
Primary vs. Dependency Tiers
To accurately map a service, the analyzer distinguishes between the core application and its supporting infrastructure using Two-Phase Discovery.
1. Primary Tier (The "Core")
These are the components that uniquely define the service.
- Example: For an Exchange service, the Primary Tier includes the servers running
MSExchangeFrontendTransport.exe. - Logic: The system scans the entire network to find these specific servers first.
2. Dependency Tier (The "Support")
These are generic components that support the service but are not unique to it.
- Example: An SQL Server or IIS Web Server. Many services use SQL, so simply searching for "SQL" would return hundreds of irrelevant servers.
- Logic: The system does not scan the whole network for these. Instead, it analyzes the outbound connections from the Primary Tier servers. It only includes a Dependency Tier server if a Primary server is actively talking to it.
This approach ensures you map the specific SQL server used by this Exchange instance, rather than every SQL server in the company.
Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Select a Pattern
From the Business Service Analyzer dashboard, navigate to the Service Patterns library. Here you can see all available templates for detecting enterprise services.
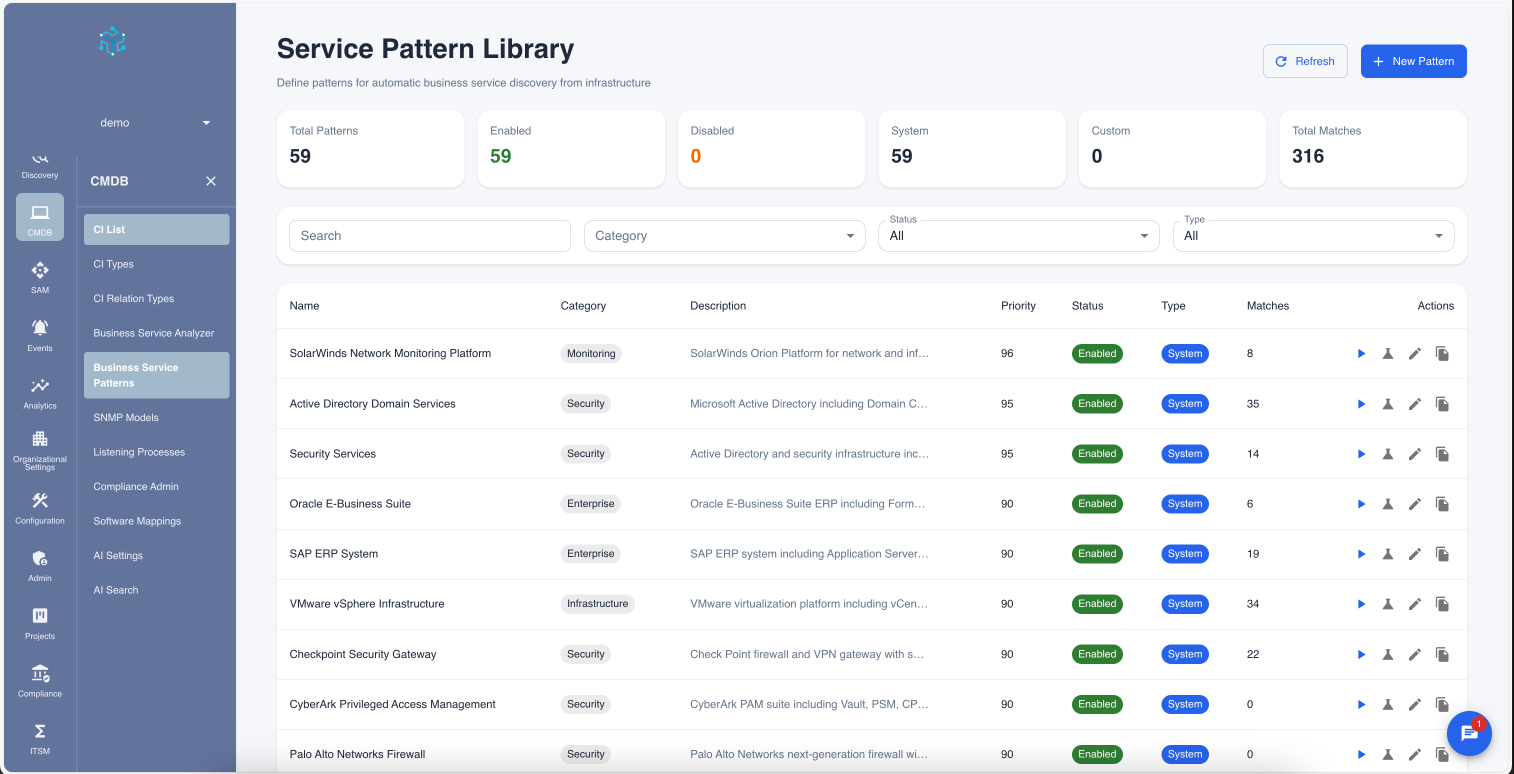 Figure 1: Browsing the Service Pattern Library.
Figure 1: Browsing the Service Pattern Library.
Step 2: Review and Customize
Before running discovery, you can review the specific criteria the pattern uses.
- Primary Tier (Blue): The unique processes or software that identify the core service.
- Dependency Tier (Orange): Common supporting services (like SQL or IIS) that are only relevant if connected to the primary tier.
You can edit these criteria to fit your specific environment if needed.
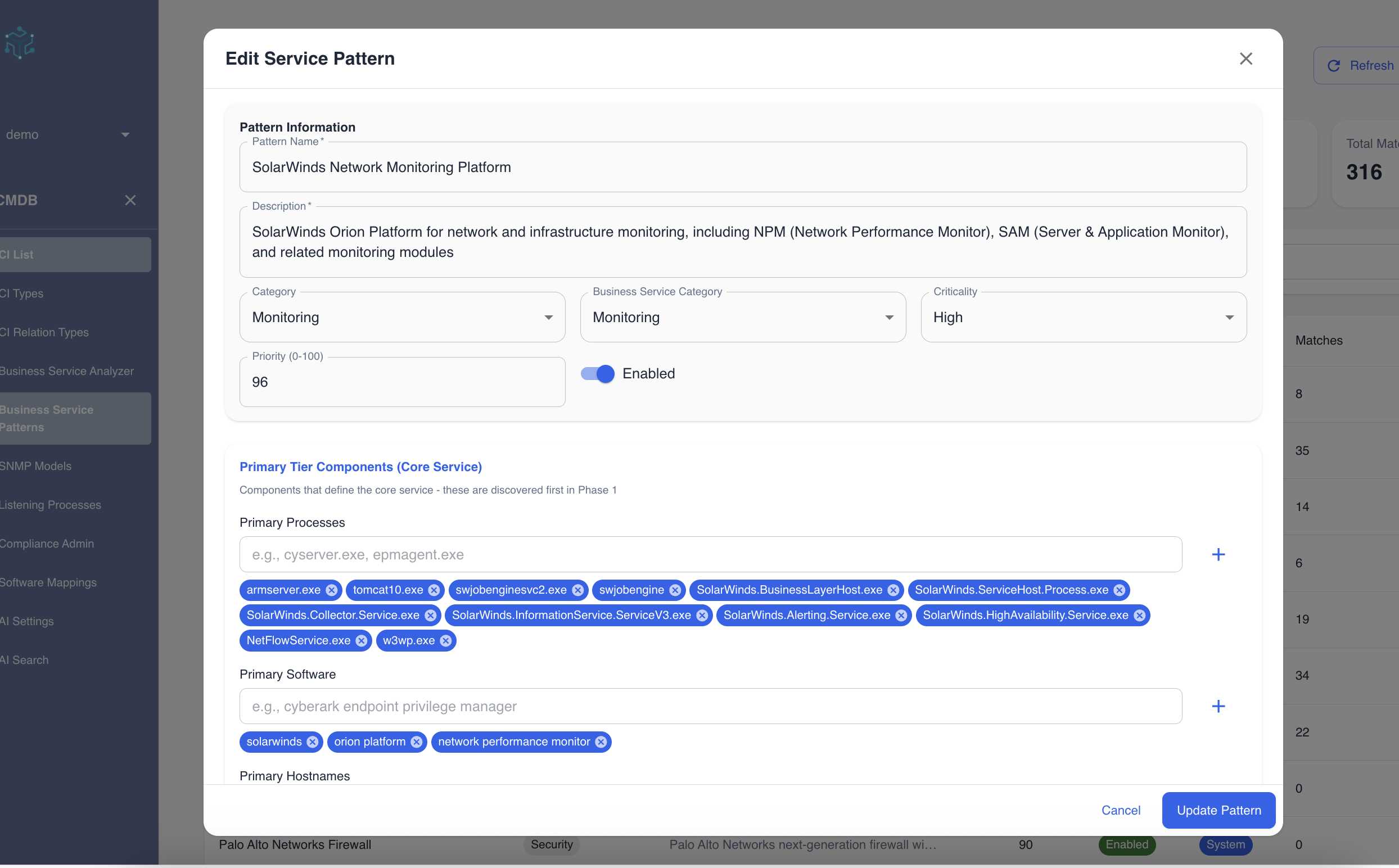 Figure 2: Reviewing primary and dependency criteria before discovery.
Figure 2: Reviewing primary and dependency criteria before discovery.
Step 3: Execute Discovery
Click "Use in Discovery" or "Proceed" to run the scan. The system will execute the two-phase discovery logic and present a mapped view of the service instance found.
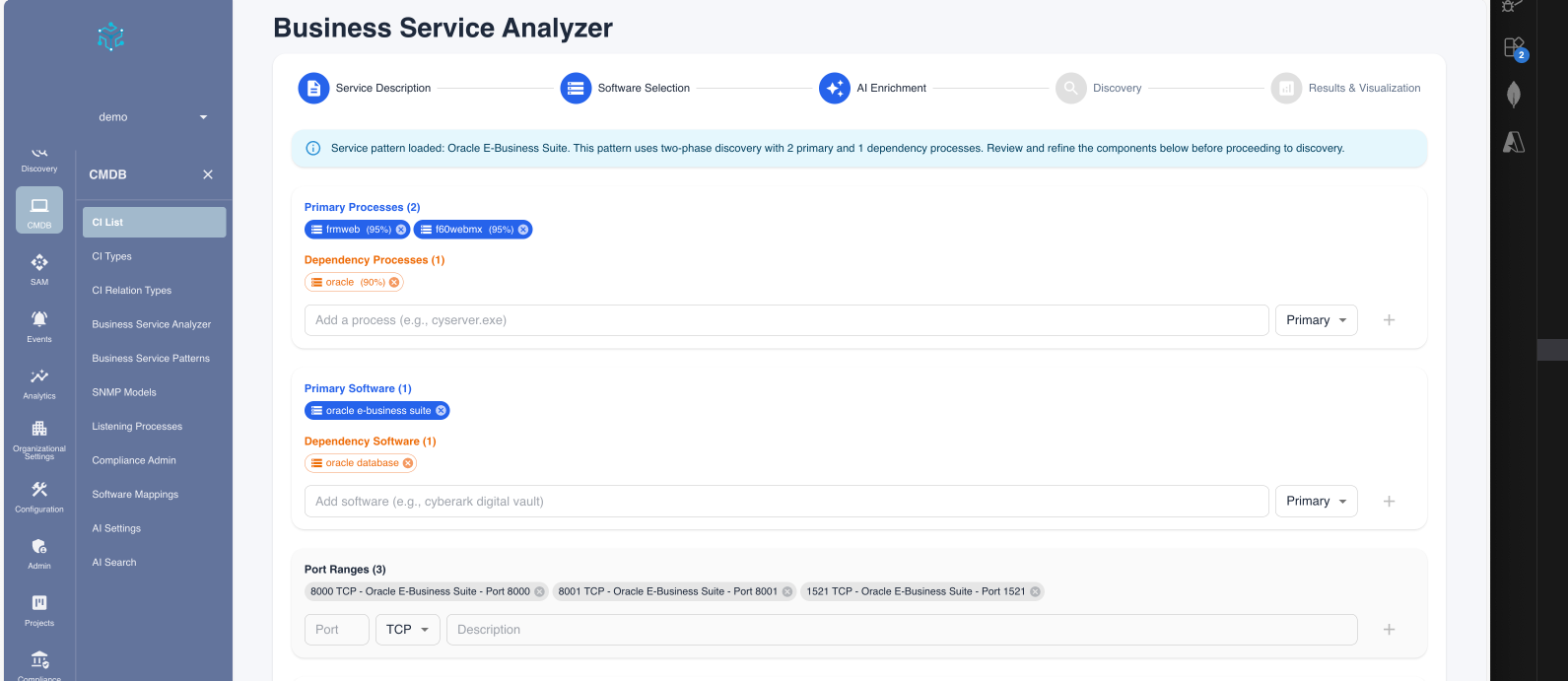 Figure 3: Viewing the discovered service map generated from the pattern.
Figure 3: Viewing the discovered service map generated from the pattern.