Visualizing CI Relationships
Understanding the connections between your Configuration Items (CIs) is crucial for impact analysis, troubleshooting, and security. The "Relationships" tab in the CI Details view provides a powerful set of tools to visualize and explore these connections.
How Relationships Are Formed
Relationships in the CMDB are created in two primary ways:
- Automated Discovery: The Tripl-i Scanner Agent automatically detects connections by analyzing network traffic and running processes on your servers. When it sees
service-a.exeon one server talking toservice-b.exeon another, it records this as a relationship. This data is sent to the platform and populates the graph. This is the most common and powerful way to build the relationship map. - Manual Creation: You can manually define a relationship between two CIs directly from the relationship graph interface. This is useful for documenting dependencies that are not easily discovered automatically, such as logical dependencies or business process connections.
The Standard Relationship View
This is the default view on the "Relationships" tab, showing direct, discovered connections.
The Relationship Graph
The primary tool is an interactive graph that displays the selected CI at the center and maps its upstream and downstream relationships.
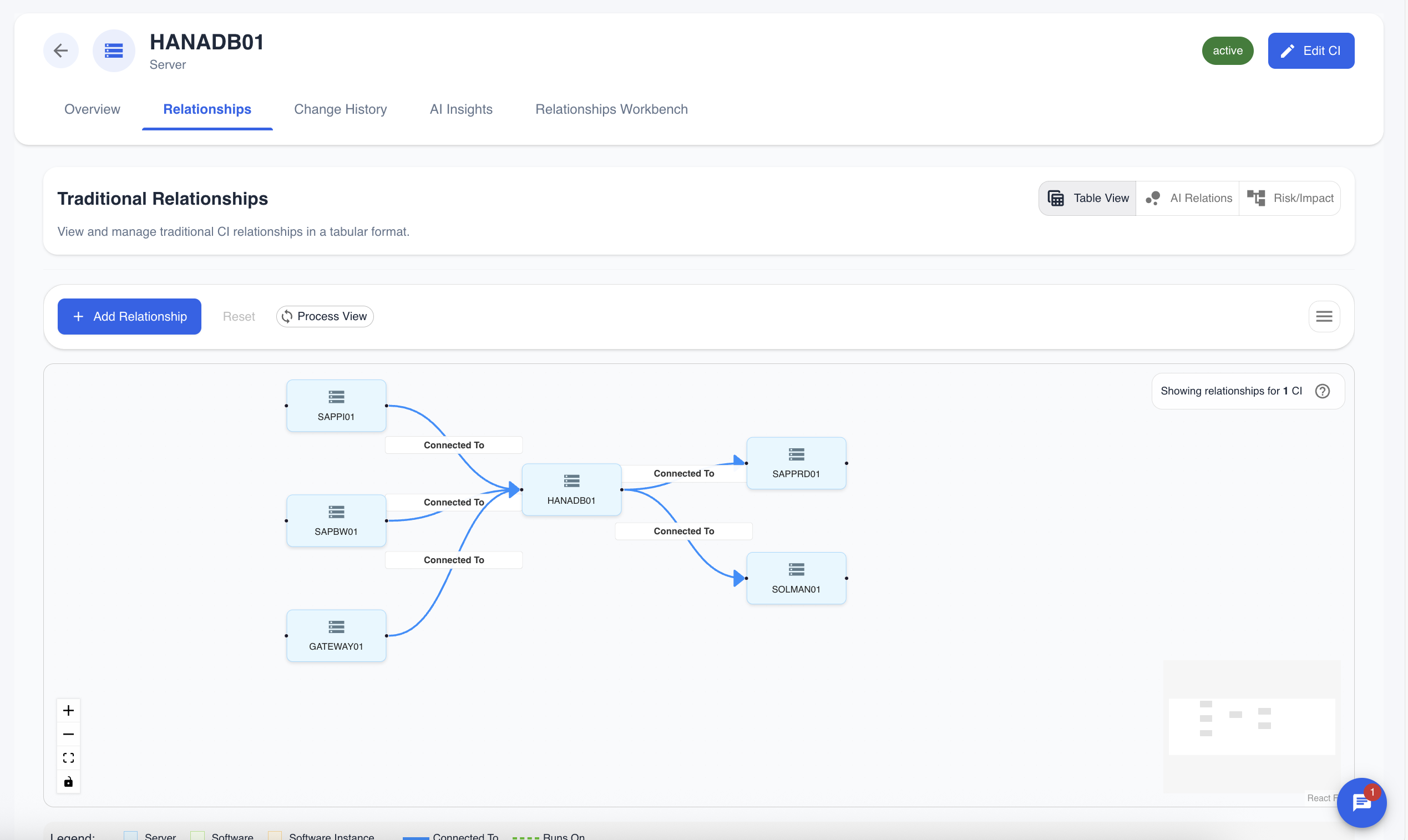
- Nodes: Each box on the graph represents a CI.
- Edges: The lines connecting the nodes represent the relationships, with arrows indicating the direction of the dependency or connection. The styling of the line indicates its type (e.g., blue for network connections, green for application dependencies).
- Interactivity: You can pan, zoom, and drag nodes to rearrange the graph for better clarity.
Process-Based View
For a more granular, application-aware perspective, you can toggle the Process View. This is a powerful feature that enriches the graph by showing not just that two servers are connected, but which specific services are responsible for the connection.
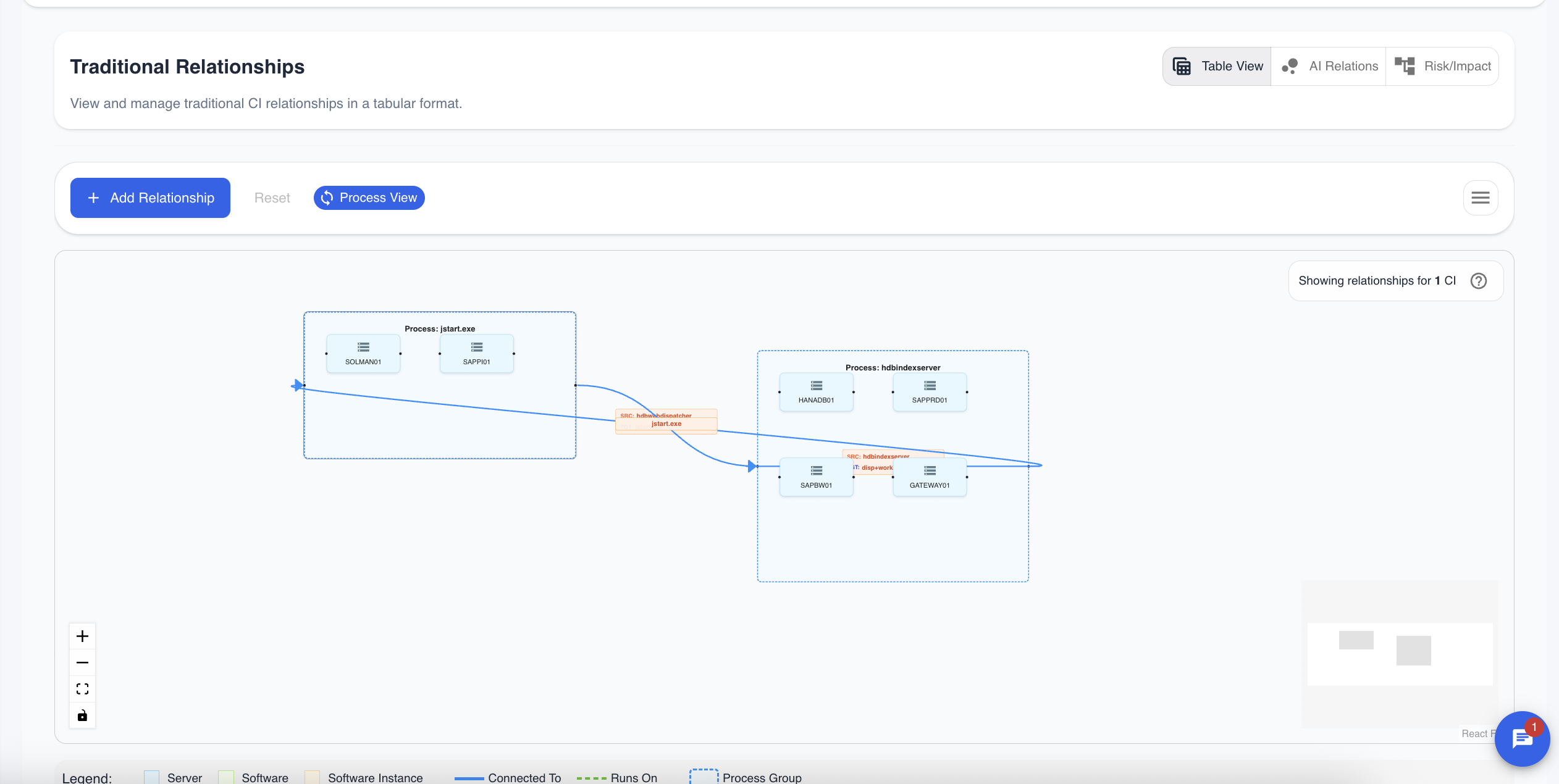
When enabled, the edges on the graph are labeled with the name of the running process (e.g., nginx.exe, sqlserver.exe) that is creating the network connection. This is invaluable for understanding application-level communication flows.
The Tabular View
Below the graph, the same relationship data is presented in a table format, separated into Outbound (connections originating from the current CI) and Inbound (connections coming into the current CI) tabs. This view provides the most detail about each connection.
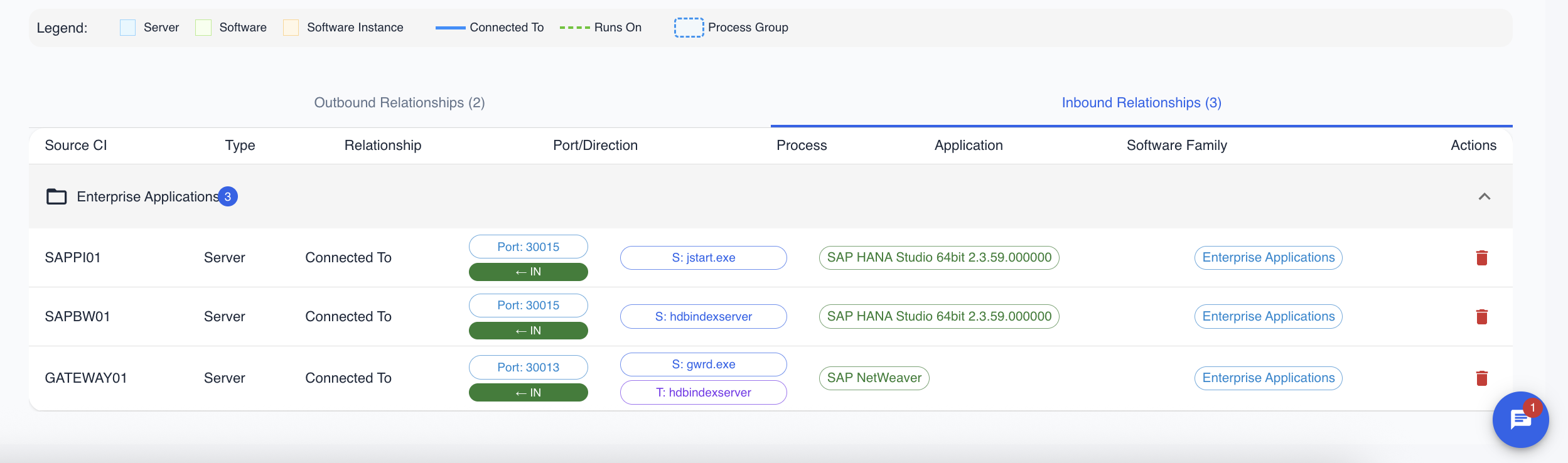
Key columns include:
- Target/Source CI: The other CI in the relationship.
- Relationship: The type of connection (e.g.,
Connected To,Depends On). - Process: The specific executable or service involved in the connection.
- Application: The software application associated with the relationship, if known.
- Software Family: If the application is part of a larger software suite (e.g., Microsoft SQL Server), it is listed here. This allows for grouping related connections.
AI-Powered Relationship Analysis
The "AI Insights" tab offers an even more advanced analysis of CI relationships. This view moves beyond simple connections to provide rich, contextual analysis generated by the Tripl-i AI engine.
How AI Analysis Works
The AI does not analyze relationships in your browser. When you click the "AI Analyze" button, the frontend gathers the IDs of all discovered relationships for the current CI and sends them to the backend. The AI engine on the server then processes this data, enriching each relationship with a deeper level of understanding. The results are then sent back and displayed in the UI.
Understanding AI Risk and Impact
The AI assigns a risk and business impact level to each relationship. These are not just arbitrary labels; they represent the AI's assessment of the connection's importance.
- Critical: Represents a relationship that is absolutely essential for a business service to function. The failure of a critical relationship would likely cause an immediate and significant outage (e.g., a web server's connection to its primary user database).
- High: A very important relationship that could cause a significant disruption if it failed, but may have some redundancy or a less immediate impact than a critical one.
- Medium/Low: Supporting relationships that are part of the overall service but are less likely to cause a major outage on their own.
AI Relationship Views
The AI analysis is presented in two ways: a detailed list and a color-coded graph.
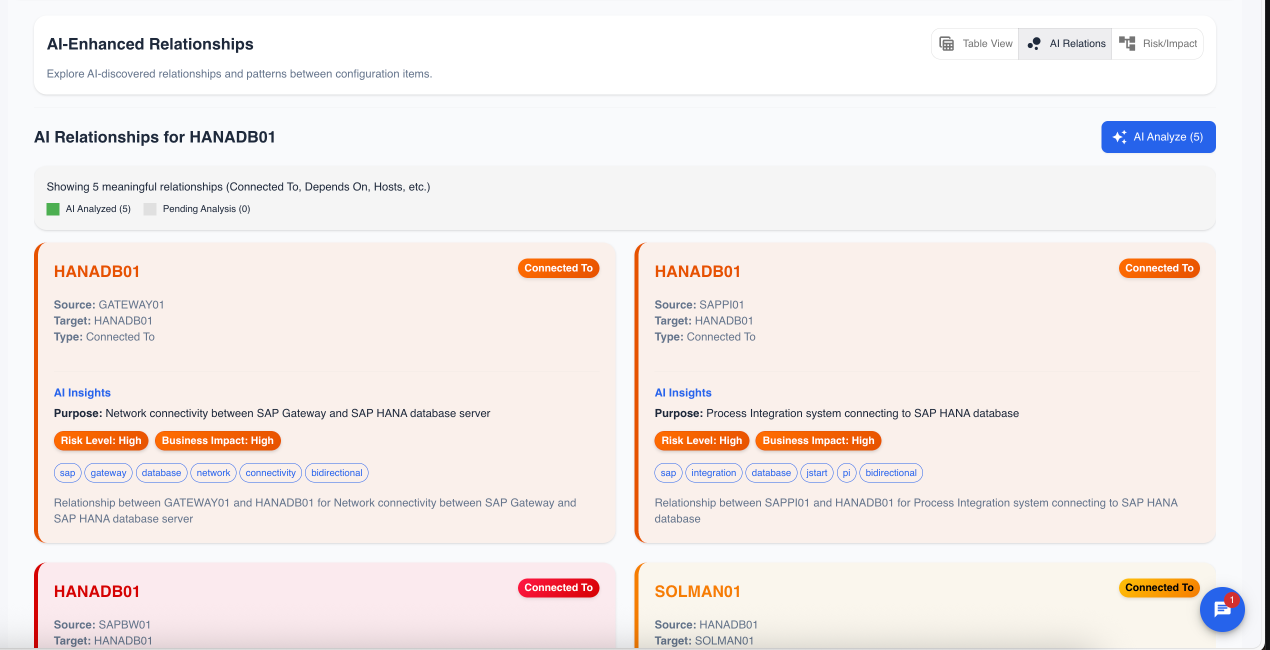
The list provides AI-generated context for each connection:
- Purpose: A plain-language description of why the connection exists (e.g., "Authentication," "Database Query").
- Risk Level & Business Impact: The AI's assessment of the connection's importance.
- Tags: Descriptive tags for quick categorization (e.g.,
bidirectional,remote-management).
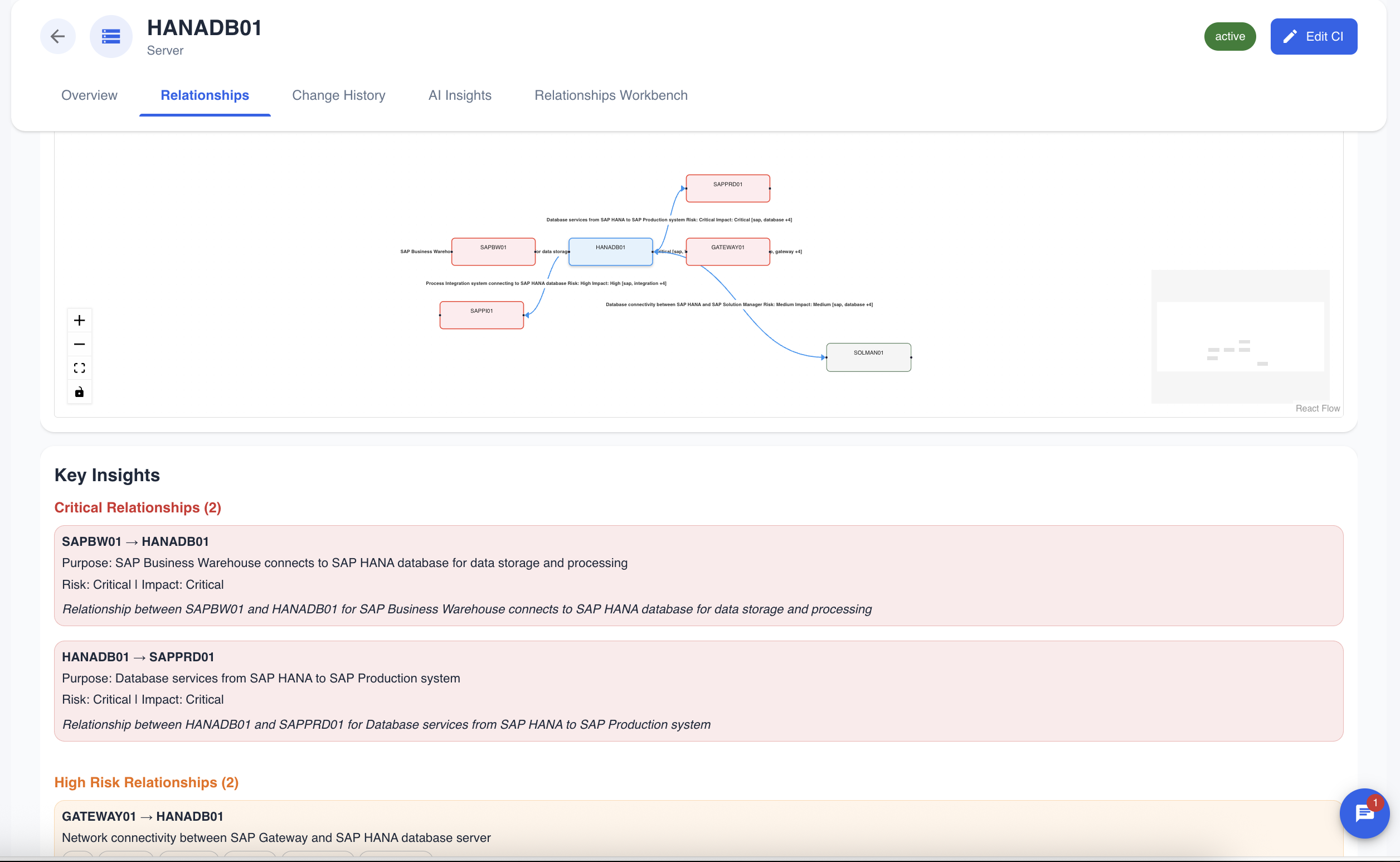
The AI graph differs from the standard graph in a key way: styling represents risk, not connection type.
- Standard Graph: Edge color and style show the type of connection (network, dependency, etc.).
- AI Graph: Edge color and thickness show the importance of the connection. Critical relationships are highlighted with thick, red lines, while low-risk connections are thin and grey. This allows you to see the most critical dependencies at a glance, regardless of the underlying technology.