Scanner GUI Guide
This guide provides a walkthrough of the Tripl-i Scanner Agent's graphical user interface (GUI). A logical workflow is to configure integrations first, then credentials, and then proceed with scanning.
This guide covers the main tabs in a logical workflow: Integrations, Credentials, Scan, Scheduler, and Service.
1. Configuring Integrations (Integrations Tab)
Before you can upload scan results, you must connect the scanner to your central Tripl-i platform. This is done in the Integrations Tab.
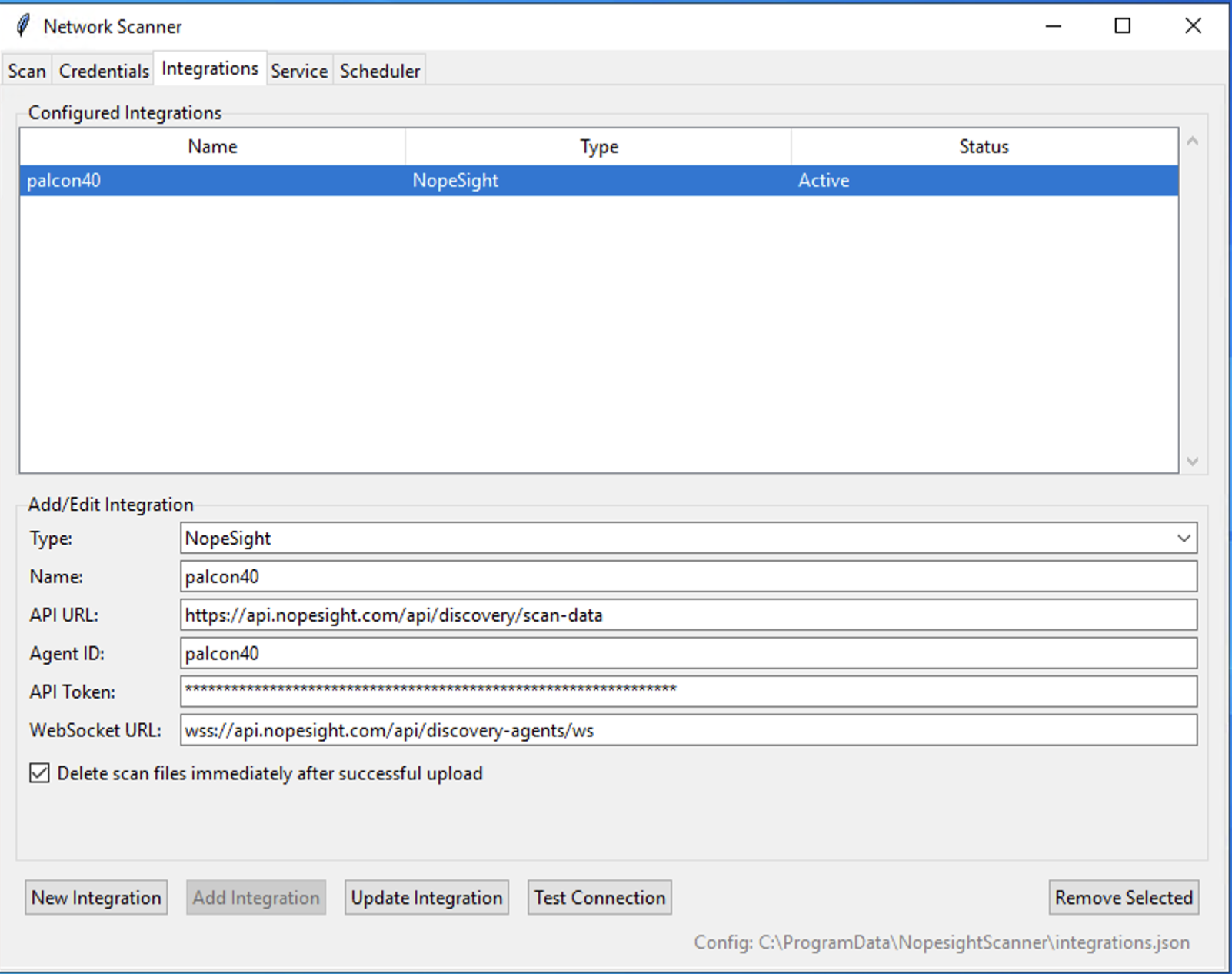
How to Configure the Integration
- Name the Integration: Give the configuration a descriptive Name (e.g., "Tripl-i Production").
- Enter API URL: In the API URL field, enter the address of your Tripl-i backend.
- Enter Agent ID: Provide a unique ID for this scanner agent. This helps identify the source of the data in the platform.
- Enter API Token: Paste the API Token (also called a Discovery Token) that you generated in the Tripl-i platform.
- Enter WebSocket URL (Optional): If your environment uses a separate URL for real-time communication, enter it here.
- Save: Click Add Integration to save the configuration.
- Test: Use the Test Connection button to verify that the scanner can successfully communicate with the Tripl-i platform.
2. Managing Credentials (Credentials Tab)
The Credentials Tab is where you securely store and manage the credentials required for the scanner to access and inventory your target systems.
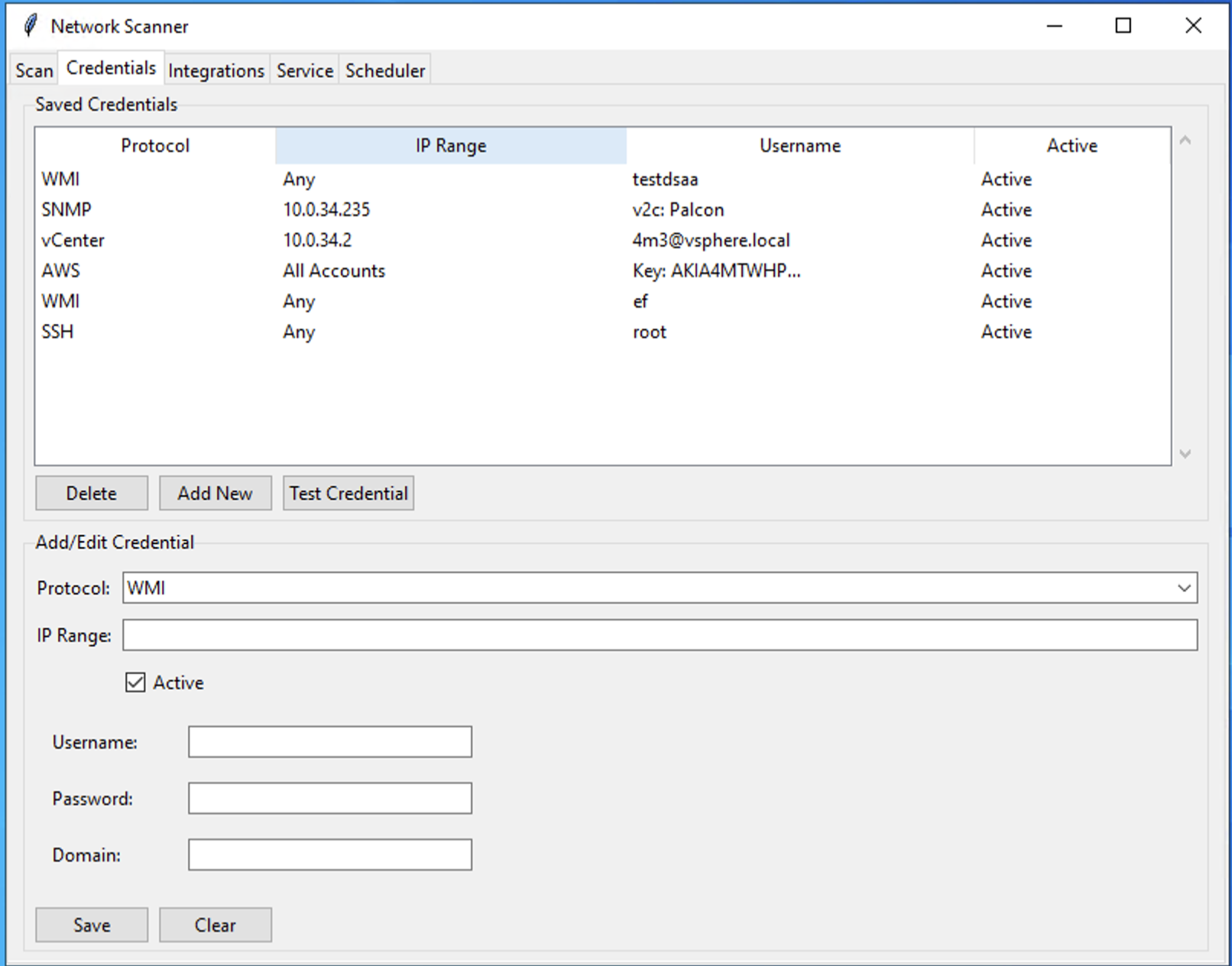
How to Add a New Credential
-
Select Protocol: From the Protocol dropdown menu, choose the type of credential you want to add (e.g.,
WMIfor Windows,SSHfor Linux,SNMPfor network devices). The fields in the form will change based on your selection. -
Enter Credential Details: Fill in the required information.
- For WMI: Enter a
Username,Password, and optionalDomain. - For SSH: Enter a
Usernameand either aPasswordor a path to an SSHKey File. - For SNMP: Select the
Version. For v1/v2c, enter aCommunitystring. For v3, fill in the detailed user, authentication, and privacy fields. - For vCenter: Enter the
UsernameandPasswordfor your vCenter server.
- For WMI: Enter a
-
Define Scope (Optional): In the IP Range field, you can enter a network range in CIDR notation (e.g.,
192.168.1.0/24). This restricts the credential to only be used for targets within that range. Leave this field blank to allow the credential to be used for any target. -
Set as Active: Ensure the Active checkbox is checked. The scanner will only use active credentials.
-
Save: Click the Save button. The new credential will appear in the "Saved Credentials" list.
Testing a Credential
Before running a full scan, you can test a credential to ensure it works.
- Select a Credential: Click on a credential in the "Saved Credentials" list.
- Click Test: Click the Test Credential button.
- Enter Target IP: A dialog box will appear. Enter the IP address of a single target machine you want to test the credential against.
- Confirm: Click "OK". A message will appear indicating whether the connection was successful or not.
3. Running a Manual Scan (Scan Tab)
The Scan Tab is where you define your scan targets and launch an immediate discovery process.
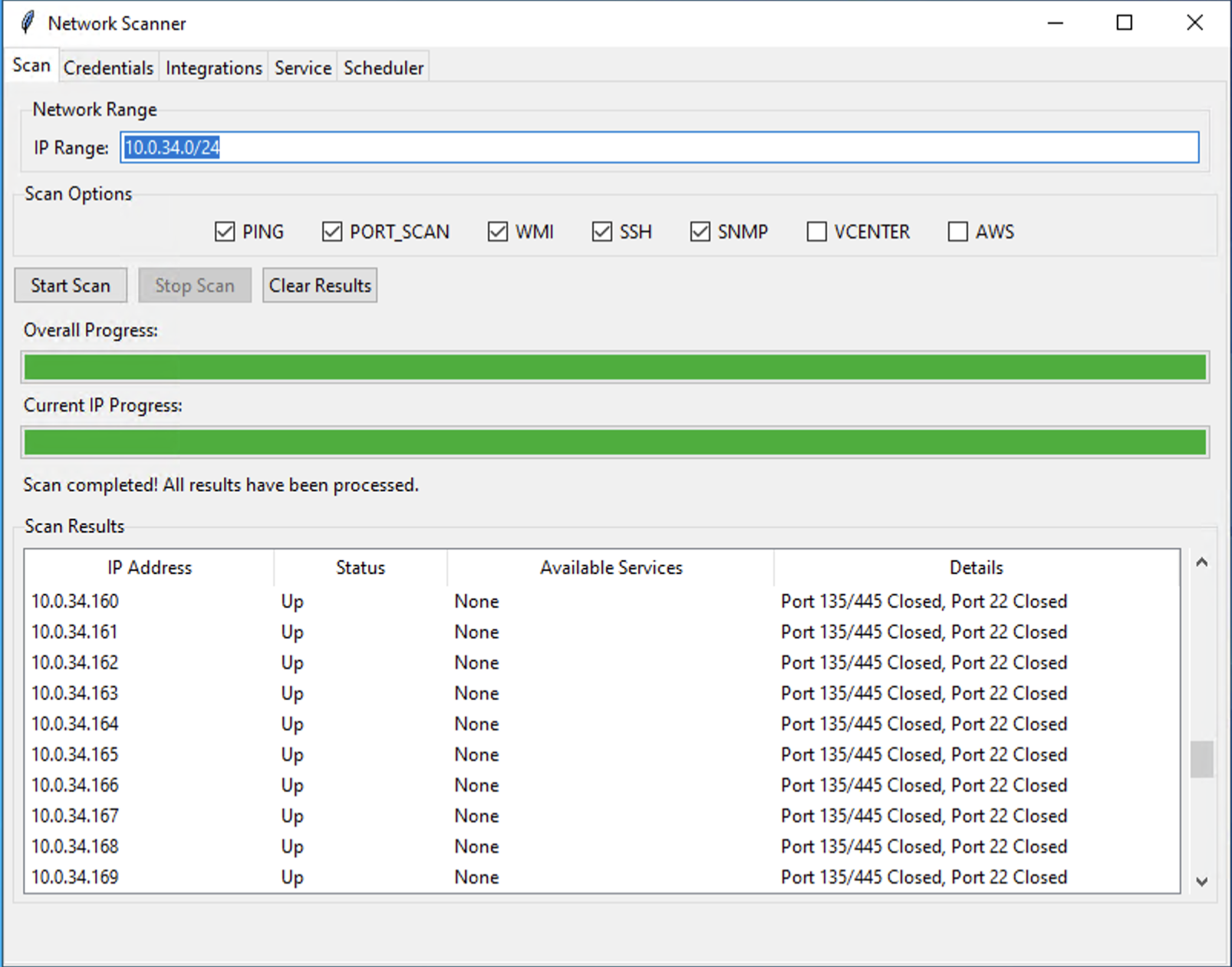
How to Run a Scan
-
Enter IP Range: In the IP Range field, enter the network(s) or IP address(es) you want to scan. The following formats are supported:
- Single IP:
192.168.1.10 - Comma-separated IPs:
192.168.1.10, 192.168.1.11 - IP Range:
192.168.1.1-192.168.1.100 - CIDR Notation:
192.168.1.0/24
- Single IP:
-
Select Scan Options: Check the boxes for the protocols you want to use during the scan. The scanner will automatically use the appropriate saved credentials for each selected protocol.
- Ping: Checks if hosts are online.
- Port Scan: Scans for open TCP and UDP ports to identify potential services.
- WMI, SSH, SNMP, vCenter: Performs deep discovery using the selected protocol.
-
Start the Scan: Click the Start Scan button. The scan will begin, and the progress bars will update as it runs.
-
Monitor Results: As devices are discovered, they will appear in the Scan Results table in real-time.
-
Stop the Scan: You can click the Stop Scan button at any time to safely terminate the discovery process.
Understanding the Results Table
- IP Address: The IP address of the discovered device.
- Status: The device's current state, typically
UporDown. - Available Services: A list of services and protocols detected on the device (e.g., WMI, SSH, HTTPS).
- Details: A summary of the scan outcome. This may show which protocol was successfully used (e.g., "SSH"), a reason for failure (e.g., "Access Denied"), or simply confirm the host is online ("Host Up").
Scanning Workflow
When a scan is initiated, the agent follows a multi-step process to discover and inventory a device.
4. Automating Scans (Scheduler Tab)
The Scheduler Tab allows you to configure automated scans that run at specific times or intervals, so you don't have to run them manually.
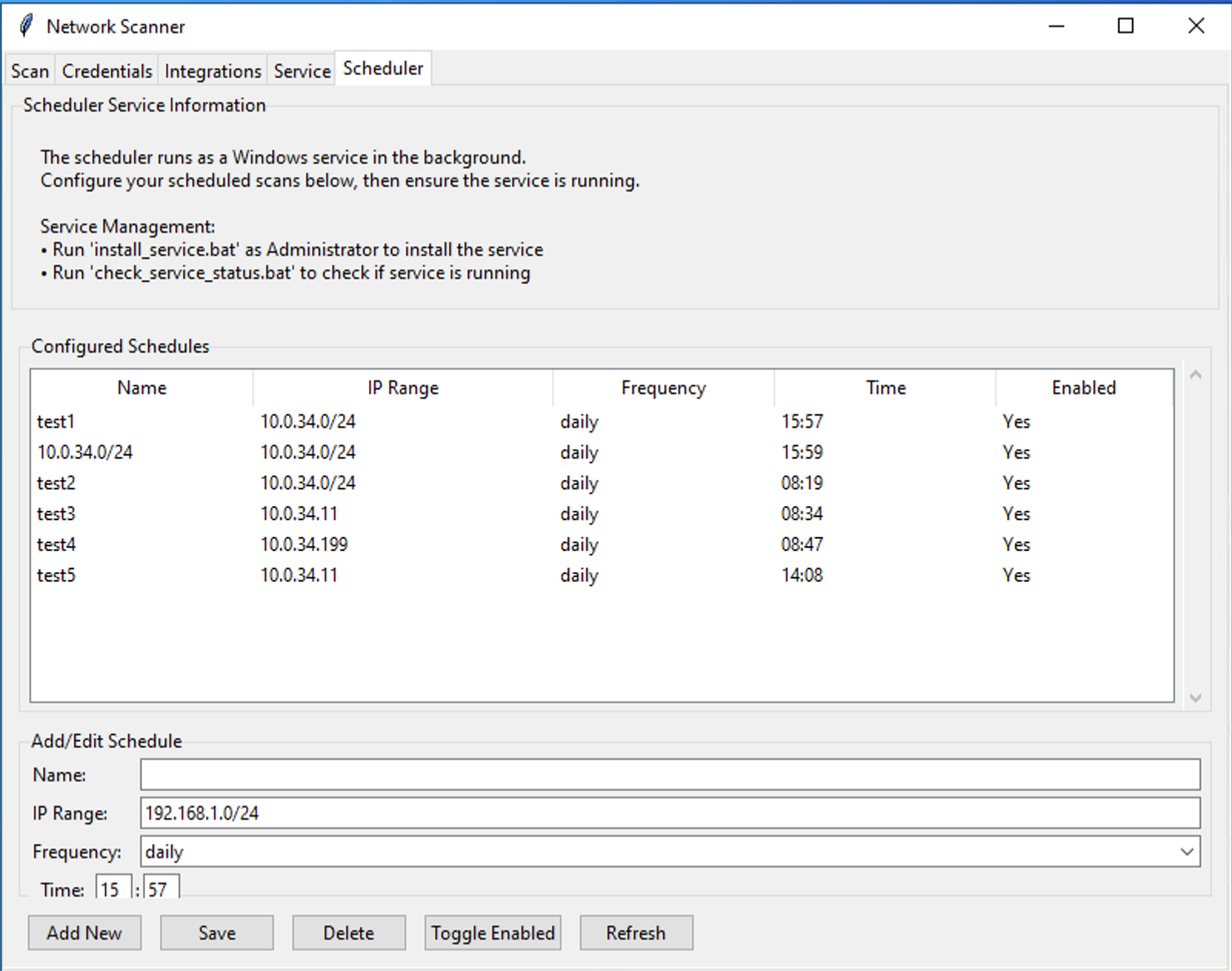
How to Add a Schedule
- Name the Schedule: In the "Add/Edit Schedule" form, give your schedule a descriptive Name.
- Enter IP Range: Define the target network in the IP Range field (e.g.,
10.0.0.0/16). - Set Frequency: Choose how often the scan should run from the Frequency dropdown:
hourly: Runs at a set interval of hours.daily: Runs once a day at a specific time.weekly: Runs on specific days of the week.monthly: Runs on a specific day of the month.
- Set Time/Interval:
- If you chose
hourly, set the Interval (e.g.,6for every 6 hours). - For all other frequencies, set the Time (in HH:MM format) when the scan should start.
- If you chose
- Save: Click the Save button. The new schedule will appear in the "Configured Schedules" list.
- Enable the Service: For schedules to run, the scanner must be running in the background. See the Service Tab section for instructions.
5. Managing the Scanner Service (Service Tab)
The Service Tab allows you to control how the scanner runs in the background to execute scheduled scans.
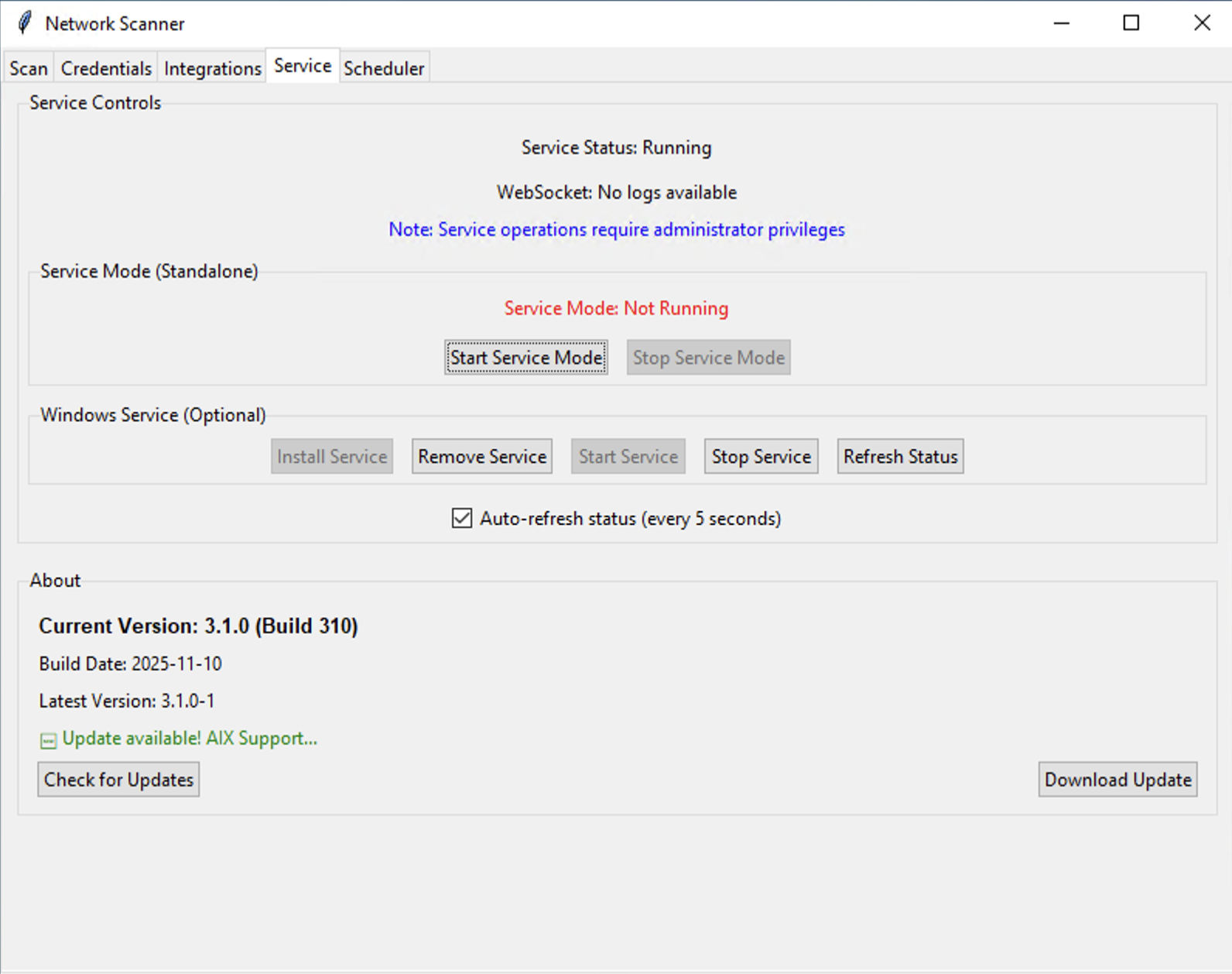
Operating Modes
Service Mode (Standalone)
This mode runs the scanner as a background process without installing it as a permanent Windows service. It's useful for testing or temporary deployments.
- Start Service Mode: Starts the background process.
- Stop Service Mode: Stops the background process.
Windows Service (Recommended)
This mode installs the scanner as a persistent Windows service that will start automatically when the system boots. This is the recommended mode for production environments. Administrator privileges are required for these actions.
- Install Service: Installs the scanner as a Windows service.
- Remove Service: Uninstalls the service.
- Start Service: Manually starts the installed service if it's stopped.
- Stop Service: Manually stops the service.