CVE Database
The CVE Database provides access to comprehensive information about Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs). This searchable database is synchronized from the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) and contains detailed information about security vulnerabilities that may affect software in your environment.
Accessing the CVE Database
- Navigate to SAM in the main menu
- Under Vulnerability Management, click CVE Database
Understanding the CVE Database
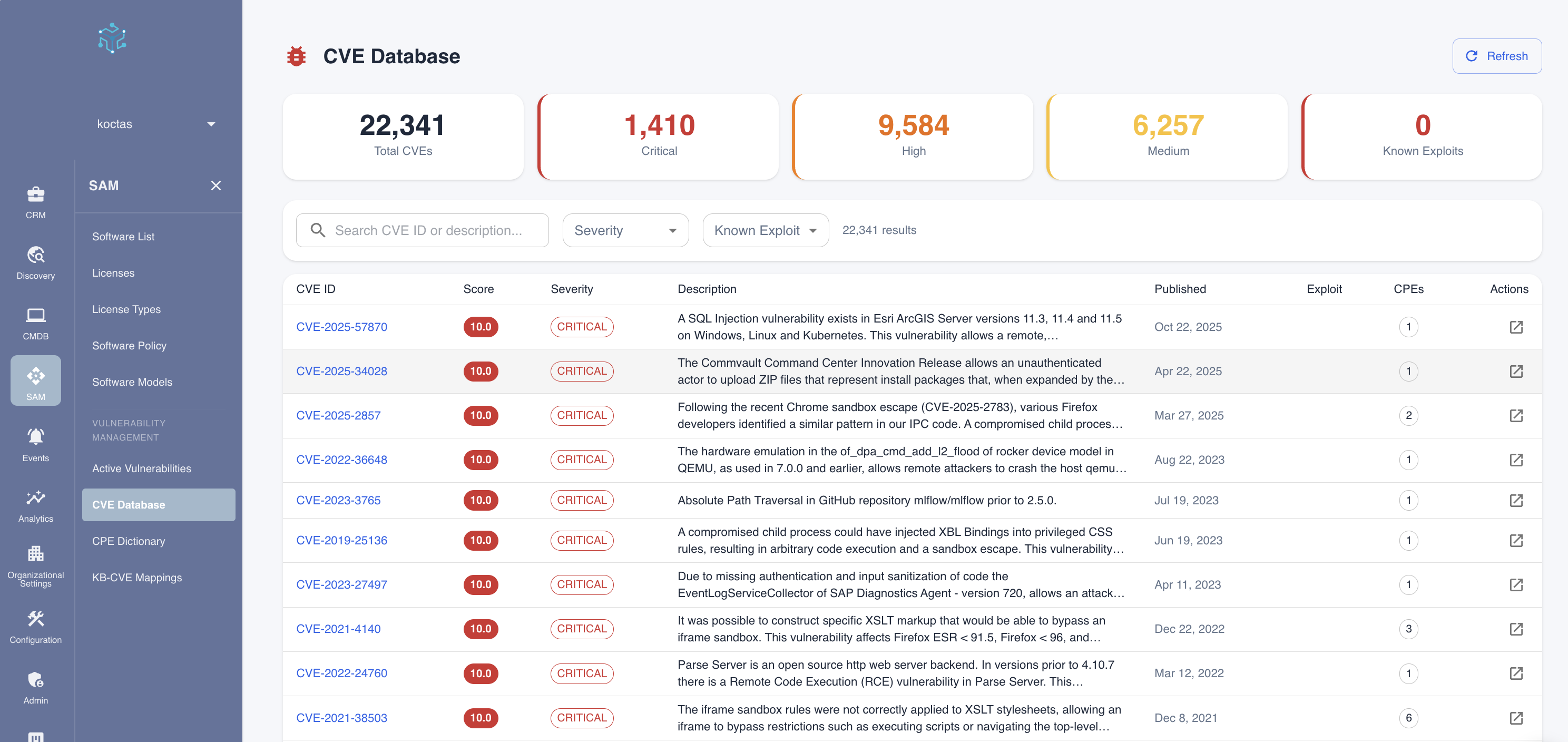
Summary Statistics
The top of the page displays key metrics about the CVE database:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Total CVEs | Complete count of CVEs in the database |
| Critical | Number of CVEs with CVSS score 9.0-10.0 |
| High | Number of CVEs with CVSS score 7.0-8.9 |
| Medium | Number of CVEs with CVSS score 4.0-6.9 |
| Known Exploits | CVEs with confirmed exploit code available |
Search and Filters
Use the search bar and filters to find specific vulnerabilities:
- Search: Enter a CVE ID (e.g., "CVE-2024-1234") or keywords from the description
- Severity: Filter by severity level (Critical, High, Medium, Low)
- Known Exploit: Filter to show only vulnerabilities with confirmed exploits
Reading CVE Entries
Each CVE entry in the table displays:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| CVE ID | Unique identifier in format CVE-YYYY-NNNNN |
| Score | CVSS score from 0.0 to 10.0 |
| Severity | Color-coded severity badge |
| Description | Brief explanation of the vulnerability |
| Published | Date the CVE was first published |
| Exploit | Indicator if exploit code is known to exist |
| CPEs | Number of affected products/platforms |
| Actions | View full details |
CVSS Scoring
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) provides a standardized way to measure severity:
| Score Range | Severity | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| 9.0 - 10.0 | 🔴 Critical | Immediate remediation required |
| 7.0 - 8.9 | 🟠 High | Remediate within days |
| 4.0 - 6.9 | 🟡 Medium | Plan remediation |
| 0.1 - 3.9 | 🟢 Low | Remediate as resources permit |
Viewing CVE Details
Click on any CVE ID or the action button to view complete details:
Vulnerability Information
- Full Description: Detailed explanation of the security issue
- Attack Vector: How the vulnerability can be exploited (Network, Local, etc.)
- Attack Complexity: Difficulty of exploitation
- Privileges Required: Access level needed to exploit
- User Interaction: Whether user action is needed
Affected Products
- List of software products and versions affected
- CPE identifiers for each affected product
- Version ranges that are vulnerable
References
- Links to vendor advisories
- Patch information
- Security bulletins
- Research papers or blog posts
CVSS Vector
The CVSS vector string breaks down the scoring:
CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
| Component | Meaning | Values |
|---|---|---|
| AV | Attack Vector | Network, Adjacent, Local, Physical |
| AC | Attack Complexity | Low, High |
| PR | Privileges Required | None, Low, High |
| UI | User Interaction | None, Required |
| S | Scope | Unchanged, Changed |
| C | Confidentiality Impact | None, Low, High |
| I | Integrity Impact | None, Low, High |
| A | Availability Impact | None, Low, High |
Using the CVE Database
Research Vulnerabilities
Before deploying new software or updates, search for known vulnerabilities:
- Search by software name or vendor
- Review severity levels and descriptions
- Check if patches are available
Investigate Alerts
When security tools flag potential issues:
- Search for the specific CVE ID
- Understand the attack vector and impact
- Determine if your environment is affected
Compliance Reporting
For security audits and compliance:
- Search for CVEs affecting critical systems
- Export findings for documentation
- Track remediation progress
CVE Synchronization
The CVE database is synchronized from the National Vulnerability Database. Navigate to CVE Sync Dashboard to manage synchronization settings and monitor progress.
Synchronization Modes
Choose the appropriate sync mode based on your needs:
| Mode | Description | Use Case | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft KB Sync | Syncs CVEs linked to Microsoft security patches | Windows patching updates | ~1-2 min |
| NVD Delta Sync | Fetches CVEs modified in the last 7 days | Daily maintenance (recommended) | ~3-10 min |
| New Software Only | Enriches software with no vulnerability data | One-time backfill or after adding software | Variable |
| Full Sync | Complete synchronization of all modes | Initial setup or repair | ~30+ min |
Understanding Each Mode
Microsoft KB Sync is ideal for Windows-focused environments. It:
- Syncs the latest KB-to-CVE mappings from Microsoft
- Updates patch coverage information
- Runs quickly and should be done weekly after Patch Tuesday
NVD Delta Sync is the recommended daily sync. It:
- Fetches only CVEs modified in the last 7 days
- Updates existing CVE records with new information
- Matches newly discovered CVEs to your software catalog
- Efficient for ongoing maintenance
New Software Only targets unenriched entries. It:
- Finds software catalog entries with no vulnerability data
- Fetches CVEs specifically for those products
- Best for initial setup or after major software deployments
Full Sync combines all modes for comprehensive coverage. It:
- Runs all sync modes in sequence
- Best for initial setup or troubleshooting data issues
- Not needed for regular maintenance
Recommended Sync Schedule
For optimal vulnerability coverage:
| Frequency | Sync Mode | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | NVD Delta Sync | Catch newly disclosed and modified CVEs |
| Weekly | Microsoft KB Sync | Align with Windows Patch Tuesday (2nd Tuesday) |
| As needed | New Software Only | After discovering new software products |
| Quarterly | Full Sync | Comprehensive database refresh |
Running a Sync
- Navigate to SAM > Vulnerability Management > CVE Sync Dashboard
- Select your preferred sync mode from the dropdown
- Review the preview showing what will be synced
- Click Start to begin synchronization
- Monitor progress in real-time with step-by-step indicators
- Review the summary when complete
Automatic Enrichment
New software discovered during scans is automatically enriched with vulnerability data from NVD. This means:
- No manual sync required for newly discovered software
- CVE coverage begins immediately after discovery
- Works for all vendors, not just Microsoft
CVE data is sourced from NIST's National Vulnerability Database (NVD), which aggregates vulnerability information from multiple sources including software vendors, security researchers, and CERT coordination centers. Microsoft KB mappings come from the Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC).
Related Topics
- Active Vulnerabilities - Managing vulnerabilities in your environment
- CPE Dictionary - Understanding software identification
- KB-CVE Mappings - Windows patch mapping